-->
With over 10 pre-installed distros to choose from, the worry-free installation life is here! Whether you are a digital nomad or just looking for flexibility, Shells can put your Linux machine on the device that you want to use. Exclusive for LQ members, get up to 45% off per month. Click here for more info. Ubuntu 20.04 Installation Stuck. Hello i am trying to install ubuntu 20.04 and i keep getting stuck on the following screen after many many hours of waiting. Configuring the Firewall to Allow SNMP Requests. To configure the Windows Firewall to allow SNMP requests on a Windows 2008 server, perform the following steps: In the Start menu search bar, enter 'firewall' to open a Windows Firewall with Advanced Security window. In the left pane, click Inbound Rules. Locate the two SNMP Service (UDP In) rules. The Microsoft Windows implementation of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is used to configure remote devices, monitor network performance, audit network usage, and detect network faults or inappropriate access.Important The Microsoft Windows SNMP API only supports protocol versions up to SNMPv2C. It does not support any later versions of the protocol.
But the answer is v1 and v2c. I don’t think the full v2 support was compatible enough to be useful anywhere. The net-snmp package compiles nicely for sol9, and provided much more in the way of interoperability with non-sun packages. It’s been the default snmp package for Solaris since about mid-way through the 10 series.
This article describes how to configure the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Service in Windows Server 2003. This article describes how to configure SNMP agent properties, SNMP traps, and SNMP security.
Applies to: Windows Server 2003
Original KB number: 324263
Summary
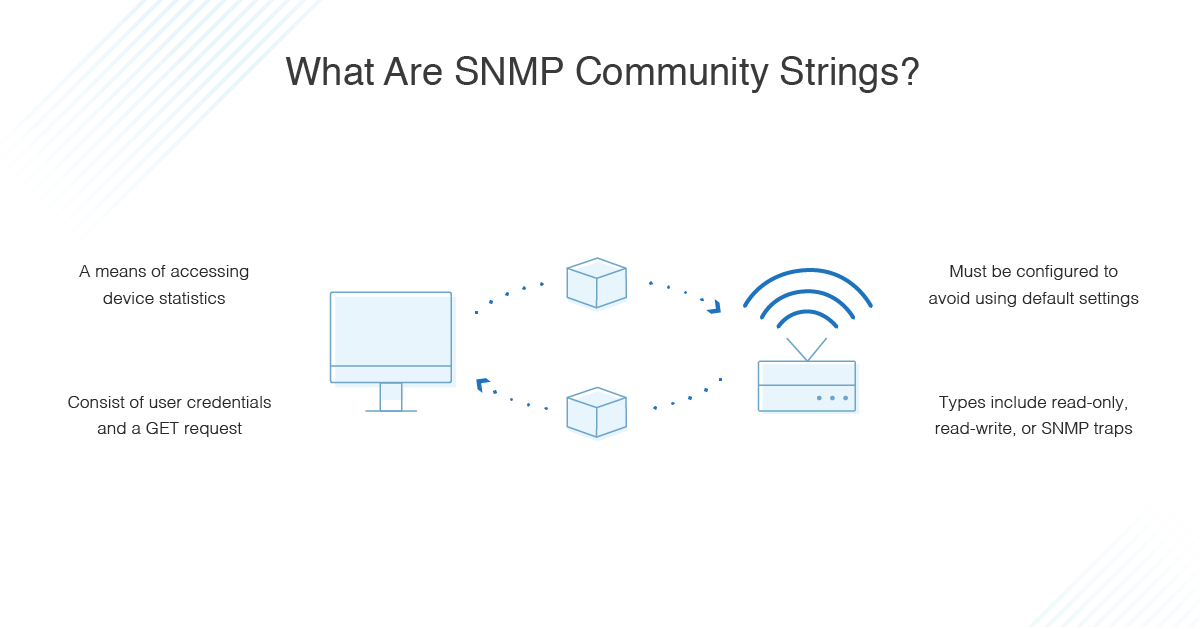
The SNMP Service, when configured for an agent, generates trap messages that are sent to a trap destination, if any specific events occur. For example, you can configure the SNMP service to send a trap when it receives a request for information that does not contain the correct community name and does not match an accepted host name for the service.
Configure SNMP agent information
Click Start, point to Control Panel, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
In the console tree, expand Services and Applications, and then click Services.
In the right pane, double-click SNMP Service.
Click the Agent tab.
Type the name of the user or administrator of the computer in the Contact box, and then type the physical location of the computer or contact in the Location box.
These comments are treated as text and are optional.
Under Service, click to select the check boxes next to the services that are provided by your computer. Service options are:
- Physical: Specifies whether the computer manages physical devices, such as a hard disk partition.
- Applications: Specifies whether the computer uses any programs that send data by using TCP/IP.
- Datalink and subnetwork: Specifies whether this computer manages a TCP/IP subnetwork or datalink, such as a bridge.
- Internet: Specifies whether this computer acts as an IP gateway (router).
- End-to-end: Specifies whether this computer acts as an IP host.
Click OK.
Note
If you have installed additional TCP/IP network devices, such as a switch or a router, see Request for Comments (RFC) 1213 for additional information. To view RFC 1213, visit the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Web site

Microsoft provides third-party contact information to help you find technical support. This contact information may change without notice. Microsoft does not guarantee the accuracy of this third-party contact information.
Configure SNMP communities and traps
Click Start, point to Control Panel, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
In the console tree, expand Services and Applications, and then click Services.
In the right pane, double-click SNMP Service.
Click the Traps tab.
In the Community name box, type the case-sensitive community name to which this computer will send trap messages, and then click Add to list.
Under Trap destinations, click Add.
In the Host name, IP or IPX address box, type the name, IP, or IPX address of the host, and then click Add.
The host name or address appears in the Trap destinations list.
Repeat steps 5 through 7 to add the communities and trap destinations that you want.
Click OK.
Configure SNMP security for a community

- Click Start, point to Control Panel, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
- In the console tree, expand Services and Applications, and then click Services.
- In the right pane, double-click SNMP Service.
- Click the Security tab.
- Click to select the Send authentication trap check box (if it is not already selected) if you want a trap message sent whenever authentication fails.
- Under Accepted community names, click Add.
- To specify how the host processes SNMP requests from the selected community, click the permission level that you want in the Community Rights box.
- In the Community Name box, type the case-sensitive community name that you want, and then click Add.
- Specify whether or not to accept SNMP packets from a host. To do so, do one of the following:
- To accept SNMP requests from any host on the network, regardless of identity, click Accept SNMP packets from any host.
- To limit the acceptance of SNMP packets, click Accept SNMP packets from these hosts, click Add, and then type the appropriate host name, IP, or IPX address in the Host name, IP or IPX address box.
- Click Add.
- Click OK.
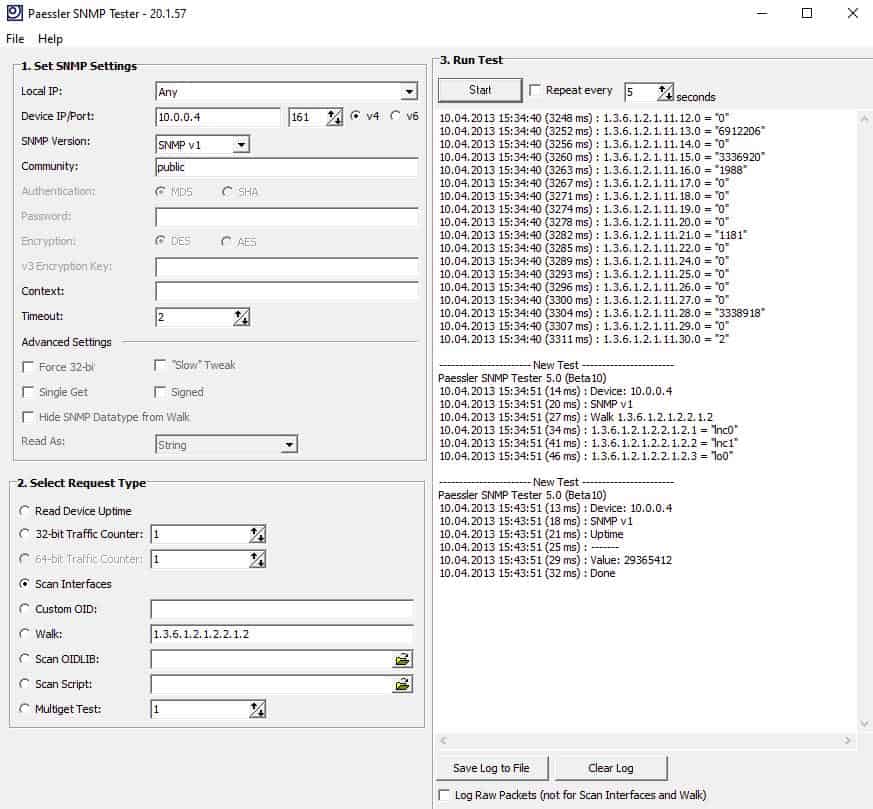
Check Snmp Version Windows 7
Important
Check Snmp Version Windows 10
If you remove all of the community names, including the default name Public, SNMP does not respond to any community names that are presented.